About the OpenTNSim-Energy module#
The OpenTNSim-Energy module calculates fuel consumption and emissions of a vessel. The method is designed in particular for vessels with one single hull, such as the tanker vessel below.
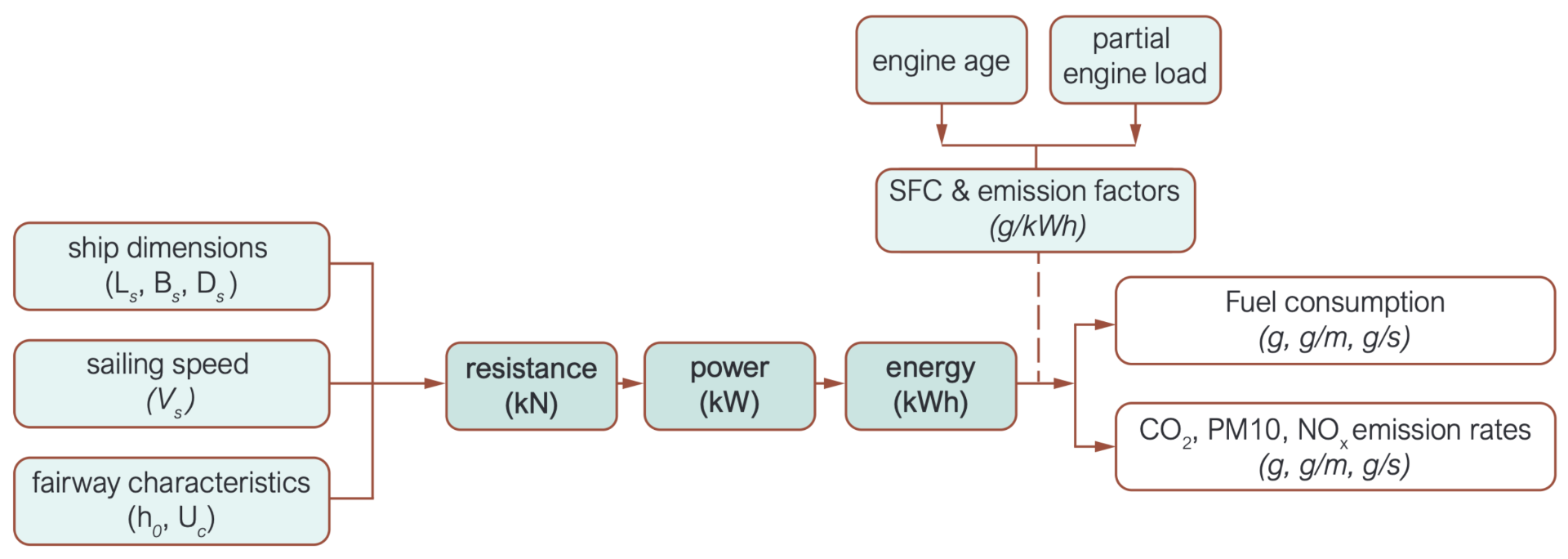
The OpenTNSim-Energy module estimates the resistance that a vessel experiences while sailing through the water with a given speed. Following the method by Holtrop and Mennen (1972), the following resistance components are estimated:
R_T = R_f (1 + k_1) + R_w + R_app + R_res
To account for shallow water effects the Karpov velocity corrections and the adjustments to the friction coefficient suggested by Zeng are added.
For each waterway section the average total resistance (R_T) is derived by estimating the friction resistance (R_f), the wave resistance (R_w), the appendages resistance (R_app) and the residual resistance (R_res) that act on the vessel at a given speed.
When we know the total resistance (kN) for the given velocity (m/s) we can work out the amount of power (kW) that the engine should deliver on average to overcome that resistance, by accounting for various efficiency and loss factors.
By multiplying this average power (kW) with the time that it is required, i.e. the time it takes the vessel to pass a given waterway section, we can derive the energy (kWh) that is needed to pass that waterway section.
With information about the engine age and the total installed power we can work out the partial engine load. Both the engine age and the partial engine load can be used to derive appropriate Specific Fuel Consumption factors (g/kWH) and Emission Factors (g/kWH). With these we can estimate fuel consumption (g, g/m, g/s) and emission rates (g, g/m g/s).
The figure below shows how the above-mentioned steps hang together:
For more information on the detailed formulae used, visit, “Part IV - Chapter 5” of the Ports and Waterways lecture notes.
